Introduction
Corporate philanthropy has gained strategic importance in recent years, particularly for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. Such companies use philanthropy to build public trust, pursue sustainable growth, and respond to various social issues (Fallah Shayan, Mohabbati-Kalejahi, Alavi, & Zahed, 2022). In capitalist countries such as South Korea, corporate social responsibility (CSR) has intensified since the late 1990s (Lim & Tsutsui, 2011). In 2008, corporate donations comprised 70% of the total funds raised by the Community Chest of Korea, highlighting an increasing trend in corporate philanthropic activities. However, few studies specifically consider the context of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. To meet this gap, this study investigates the philanthropic activities of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies from a strategic communication perspective, analyzing how they simultaneously enhance social and corporate value (Bruyaka, Zeitzmann, Chalamon, Wokutch, & Thakur, 2013). According to a report by the Federation of Korean Industries (2022), investments in corporate philanthropic activities continue to increase. We explore how such activities positively contribute to corporate performance and have social benefits (Hasan, Singh, & Kashiramka, 2022). We aim to discover differentiated strategies that effectively perform strategic CSR and promote sustainable growth.
Methods
The study was conducted in two phases. First, using press releases from the domestic Korean media, the philanthropic activities of pharmaceutical companies ranked in the top 50 in domestic sales from 2021 to 2024 were analyzed. This type of case analysis is useful for developing new theories or refining existing ones (Calderon-Monge & Ribeiro-Soriano, 2024). These activities were then classified and analyzed. Data from the third quarter of 2023 helped identify recent trends in philanthropic activities. Press releases available online as of April 2, 2024, were reviewed to identify key terms.
In the second phase, the primary classified and analyzed data were examined to establish how each company strategically conducted and promoted philanthropic activities. This analysis used secondary data, including papers and reports on strategic communication; social contribution; environmental, social, and governance activities; and CSR activities, both domestically and internationally.
Results
CSR is defined differently depending on the research focus and can encompass corporate citizenship, corporate commitment activities, and corporate philanthropic activities (Ahmad, Ahmad, Islam, & Kaleem, 2020). Bowen (1953) formulated the early definition of CSR as “the obligation of businessmen to pursue policies and decisions that conform to the goals and values of society.” (p. 6). This has become an important benchmark for researchers conceptualizing CSR. Eells and Walton (1961) and Anderson (1986) emphasized that corporations should follow ethical principles and engage in CSR. McGuire (1963) expanded this approach to include a sense of responsibility toward society as a whole. Lee and Moon (2007) noted that CSR began to take shape alongside industrialization in the 1980s. Chapple and Moon (2005) found that Korean companies have high participation in corporate philanthropy.
Recently, CSR activities have evolved from merely charitable activities to the creation of social value. This change was reflected in Kramer and Porter’s (2011) concept of creating shared values (CSV). This reflects the idea that corporate activities can have positive effects on society, highlighting the need for proactive corporate interventions in social and environmental issues.
Thus, CSR has evolved into a broad concept that includes economic, legal, social, and ethical responsibilities. Companies incorporate CSR into their relationships with various stakeholders. Through philanthropic activities, companies reaffirm their social purpose and responsibilities, thereby continuously creating social and economic value (Mu & Lee, 2023).
CSR has been discussed in several ways. Initially, this was considered contrary to a firm’s actual responsibilities (Kang & Jeon, 2011). Friedman (1962, 1970) characterized CSR as limited to maximizing shareholder profits. However, recently, the role of corporations in addressing social and environmental issues has been emphasized. In Korea, CSR activities became prevalent among industrialized firms in the 1980s (Lee & Moon, 2007). Furthermore, new forms of CSR, such as CSV, have been proposed in light of the negative effects of economic activity (Kramer & Porter, 2011).
Korean companies also participate in corporate philanthropy at the international level (Chapple & Moon, 2005) in tandem with their economic activities. By evolving beyond simple charity into social value creation, corporate philanthropy has become a critical means for firms to fulfill CSR and promote sustainable growth (Yoon & Lee, 2017).
Studies have also confirmed that corporate philanthropic activities positively affect brand equity and customer loyalty (Han, 2021). Thus, the authenticity of social contributions plays a critical role in stakeholder relationships. Accordingly, there is growing awareness that companies should focus not only on generating economic benefits but also on creating social value (Choi, Choi, Bae, & Jeong, 2023).
Individual consumer tendencies and lifestyles affect CSR-related perceptions and purchasing behaviors (Kim & Lim, 2019). Kim and Lim (2019) reported that CSR is important for enhancing brand image and increasing purchase intentions. Yun and Jeon (2017) and Maignan and Ferrell (2004) confirmed that CSR positively influences consumer purchase intentions. These findings are supported by Han (2021), who concluded that CSR positively affects brand assets and customer loyalty.
Maruf and Afeez (2013) noted that CSR messages tend to be perceived as non-altruistic when they are abstract, underscoring the importance of delivering clear and logical CSR messages. These authors also argue that psychological factors must be considered in public evaluations of CSR activities. Carroll (2004) and Lee and Kim (2016) emphasized that CSR activities are important for securing local social legitimacy in global markets.
Firms engage in CSR activities both domestically and internationally. For example, KB Kookmin Bank expanded its philanthropic activities abroad. Gardberg, Zyglidopoulos, Symeou, and Schepers (2019) suggested that corporate philanthropic activities are likely to be interpreted negatively. However, Stanaland, Lwin, and Murphy (2011) reported that corporate philanthropic activities can positively affect consumer perceptions and that providing information via the Internet is effective. These studies indicate that philanthropic activities play a crucial role in managing corporate image and branding and are directly linked to consumers’ purchase intentions (Lee & Lee, 2018).
This study analyzes press releases related to the philanthropic activities of companies ranked in the top 50 in domestic Korean sales from 2021 to 2024. Activities were initially classified into three main categories based on themes and keywords: charitable activities, sponsorships, and volunteer work (Table 1). These were further subdivided into seven main types, as follows:
-
(1) Culture/Arts/Sports Support and Promotion: include activities that support arts organizations, exhibitions, performances, and sports events, thus enhancing cultural assets and social cohesion.
-
(2) Education/Academic Support: includes activities that improve academic research and education quality through scholarship programs, educational infrastructure improvements, and research funding support.
-
(3) Environmental Protection: includes activities that promote ecosystem protection and sustainable resource use through sustainable business practices and environmental protection projects.
-
(4) Monetary Donation: includes financial donations for disaster relief funds, social welfare programs, and health campaigns, which help strengthen the social safety net.
-
(5) Program Operations and Operational Expense Support: include activities that support the operating expenses of nonprofit organizations or social service agencies, thus helping to achieve educational, health, and social welfare goals.
-
(6) Disaster Relief: includes activities that provide necessary medical care, food, and temporary housing during natural disasters or social crises aimed at addressing urgent situations.
-
(7) Community Service: includes organizing volunteer activities that employees participate in to promote community engagement and address social issues.
This classification helps illustrate how companies’ philanthropic activities are reported and how each type of activity contributes to social goals, thus laying the foundation for long-term social impacts.
Companies strategically undertake philanthropic activities and promote them through the media. In this process, the media highlight the agents and directions of philanthropic activities and reveal them to the public (Table 2).
Individual donations typically involve successful entrepreneurs or prominent figures who donate their private wealth. Such donations reflect the donors’ personal beliefs. The media coverage focuses on individual donors and describes their contributions. Table 3 lists several examples.
Corporate foundations and corporate-initiated philanthropy involve systematic philanthropic activities conducted through foundations established by companies or internal organizations. These activities are conducted in areas such as education, environmental protection, community development, and health promotion. Through foundations, companies invest in various social value-creation activities such as scholarship program operations, infrastructure improvement, and environmental protection. This can help to promote community development and improve public health, aiming for a sustainable social impact. Thus, philanthropy has become an important means of fulfilling CSR and building close relationships with local communities. These activities are reported in press releases with the company or corporate foundation as the subject. Table 4 presents examples of philanthropic activity reports.
In cause-related marketing, companies strategically link charitable activities with profit generation to increase their profits. As social actors, companies strive to harmoniously connect their interests with those of the entire community (Luo, Zhang, & Liu, 2015) and strategically conduct philanthropic activities to ensure that profits and social development do not conflict. Cause-related marketing involves responding to consumer needs and achieving marketing goals while forming partnerships with nonprofit organizations, comprising a win–win strategy that includes philanthropic activities (Han, 2001). Table 5 presents examples of cause-related marketing.
Based on the above categories, this study analyzes the philanthropic activities of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies ranked in the top 41 in domestic sales from 2021 to 2024, as shown in Table 6.
Maignan and Ferrell (2004) characterized corporate philanthropy not only as a nonprofit-oriented activity but also as a communication process beginning within the company and extending to the media, consumers, and the public. This serves as a platform for companies to publicly express their social values and responsibilities, which are directly linked to building consumer trust. Based on the Model of Communication theory, philanthropic activities enhance communication between companies and the public in a manner similar to crisis communication through the media. This affects public perceptions and attitudes toward the company and serves as a strategic communication tool for companies as they respond to social demands and expectations and strengthen relationships with stakeholders. Thus, companies can manage their CSR activities, improve their social perceptions, and gain opportunities to enhance consumer loyalty. Such a strategic approach can guide companies in planning philanthropic activities, seeking ways to maximize social impact, and enhancing corporate value (Maignan & Ferrell, 2004). Figure 1 depicts the application of this strategy in the corporate philanthropy and communication process, which is further detailed below (Table 7).
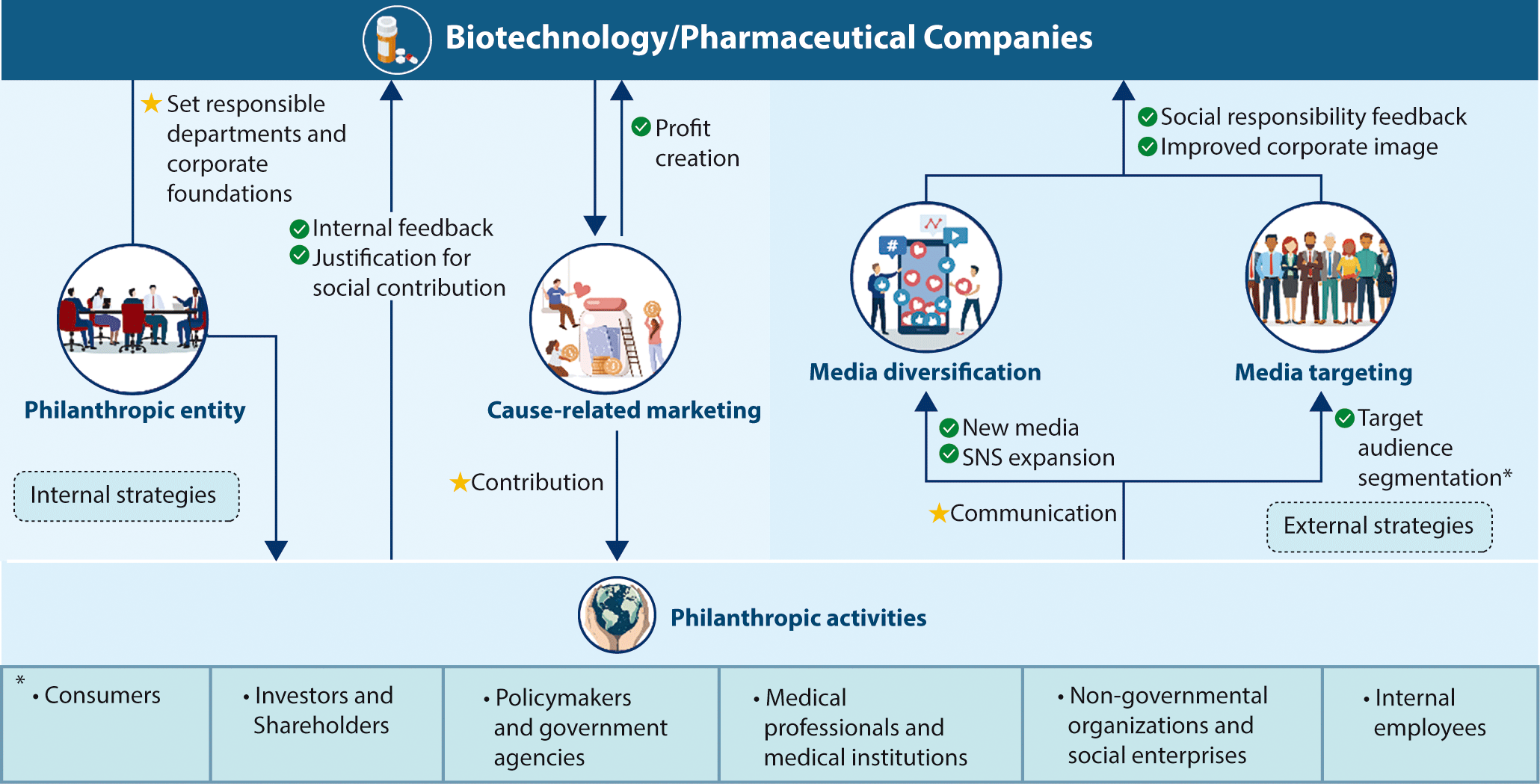
The departments or foundations responsible for a company’s philanthropic activities play a crucial role in communication by aligning the company’s strategic goals with its CSR beyond mere charity. They manage philanthropic activities systematically and professionally, enhancing internal efficiency and expertise while contributing to the company’s positive image.
Through clear communication channels, these groups ensured that the information was consistent and reliable. They strengthened their relationships with society and fostered public engagement by delivering the company’s social messages in a controlled and consistent manner. This type of structure transforms philanthropic activity from mere internal management to a bridge between the company and society, further highlighting the importance of philanthropy.
In cause-related marketing, companies use charitable activities as strategic assets to pursue corporate and social benefits. This is particularly significant for pharmaceutical companies because their products and services help improve health and quality of life. Yuhan Corporation, for example, undertook philanthropic activity by providing the drug Rexraza for free. This type of activity fulfills CSR by using a product for philanthropy, which promotes the product without incurring additional marketing costs.
The analysis indicates that pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies’ communication regarding philanthropic activities was mainly limited to distributing press releases and using corporate-owned media. Such approaches may not fully reflect diverse communication needs and could limit the effectiveness of strategic message delivery. Therefore, there is a need for a customized communication strategy based on the characteristics of the target group. Whereas social media can promote interactive engagement with younger consumer groups, traditional news media is more suitable for providing reliable information. Therefore, this study suggests that pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies should use a segmented approach tailored to different target groups for effective communication. This approach can effectively convey the company’s CSR and maximize the visibility and effect of its philanthropic activities.
Biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies have promoted philanthropic activities mainly through legacy media. However, with the rise of social media and the changes in the media landscape, there is an increasing need for media diversification and targeted messaging. Haenlein and Kaplan (2010) suggested that social media facilitates consumer engagement and effectively increases brand awareness by combining brand messages with user-generated content. This increases the touchpoints with various audiences and allows for communication tailored to the specific needs or concerns of consumers through each media channel, thereby inducing participation and response. Therefore, pharmaceutical companies should use social media to engage younger audiences through interactive content while using traditional media to provide more detailed information. This approach can help to integrate CSR with marketing goals, thereby playing a critical role in maximizing the visibility and effectiveness of a company’s philanthropic activities.
Discussion
The strategic communication of philanthropic activities by biotechnology firms plays a critical role in enhancing both social and corporate value, thereby fostering sustainable growth and reinforcing public trust. The implications of the study’s findings in the context of existing literature and theoretical frameworks are as follows:
Effective strategic communication of CSR activities is essential for biotechnology firms aiming to build and maintain a positive corporate reputation. This study corroborates and extends, in a particular context, the findings of previous research, which indicates that transparent and well-articulated CSR efforts significantly bolster stakeholder trust and loyalty (Gardberg et al., 2019). The dissemination of CSR information aligns with the principles of legitimacy theory, suggesting that organizations seek to ensure their activities are perceived as legitimate by various stakeholders, thereby enhancing their social contract (Suchman, 1995).
The findings from this study emphasize and confirm the importance of CSR communication in enhancing brand equity and consumer loyalty in the context of biotechnology firms. These efforts strategically communicate their philanthropic efforts and not only contribute to societal welfare but also strengthen the company’s market position. This dual benefit supports the resource-based view of the firm, which posits that strategic resources, including CSR initiatives, can provide competitive advantages (Barney, 1991). Studies have shown that, when effectively communicated, they lead to increased consumer trust and loyalty, which are critical components of brand equity (Stanaland et al., 2011).
Despite the evident benefits, we empirically outline that biotechnology firms face significant and unique challenges in effectively communicating their CSR activities. The study found that many firms predominantly utilize traditional media channels, which may not be effective in fully engaging a diverse audience. This finding is consistent with previous research suggesting the need for a more nuanced and multi-faceted communication strategy that includes social media to reach younger, more tech-savvy demographics, as well as traditional media to convey detailed and credible information to a wider audience (Haenlein & Kaplan, 2010).
Our findings indicate that the integration of CSR into the strategic communication framework of biotechnology firms is needed to optimize social and economic benefits. This study highlights the potential for CSR activities to enhance corporate reputation and foster consumer loyalty, thereby driving sustainable growth. Future research can further explore the economic impacts of CSR activities across different industries to provide a comprehensive understanding of their role in corporate performance in various contexts. Additionally, examining the effects of various types of CSR initiatives on consumer behavior could offer deeper insights into optimizing CSR strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the strategic communication of philanthropic activities is integral to the success of biotechnology firms. By embedding CSR within a broader strategic framework, these firms can achieve significant social and economic advantages, thereby reinforcing their competitive position in the market. This study contributes to the growing body of literature on CSR by providing a detailed analysis of its strategic importance in the biotechnology sector and underscores the need for effective communication strategies to maximize the impact of philanthropic activities.
This study illuminates empirically how pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies can enhance their social and corporate value through philanthropic activities. These findings indicate that these activities are the company’s contribution to mitigating disease and improving health, leading to positive changes in consumer health awareness and attitudes. This, in turn, contributes toward increasing customer loyalty and corporate brand value while also fulfilling CSR and building social trust.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies leverage their expertise and resources to address health issues. These activities can improve public health and are directly related to the missions of such companies. This study emphasizes that these companies generate both social and economic value by strategically designing and implementing philanthropic activities. This study’s findings indicate that these activities have a positive effect on the long-term growth and sustainability of companies.
Furthermore, this study’s analysis of how consumers perceive pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies’ philanthropic activities highlights the ways in which companies can gain consumers’ trust and enhance their preferences for their products or services. This underscores the competitive advantages and market positions that companies can achieve through philanthropic activities.
The findings show that philanthropic activities can serve as a strategic tool that goes beyond corporate ethics to contribute directly to economic performance. This has important implications for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. Enhancing the brand image and expanding the customer base through philanthropic activities can be vital for these companies as they compete in the market.






